In the competitive landscape of luxury scarf manufacturing, where brand reputation hinges on impeccable craftsmanship, automated quality control has shifted from competitive advantage to operational necessity. Consumer expectations for consistent quality and sustainability continue rising, while traditional manual inspection methods—with their inherent subjectivity and 60-75% accuracy rates—can no longer meet modern production demands. This technical roadmap, drawing on decades of industry expertise and aligning with 2025 manufacturing trends, provides scarf manufacturers a systematic approach to implementing automated quality control systems that deliver measurable improvements in defect detection, production efficiency, and cost reduction.
The Case for Automation in Scarf Quality Control
The textile industry has witnessed a transformative shift in quality assurance methodologies, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence and machine vision technologies. For scarf manufacturers specifically, this evolution addresses several longstanding challenges unique to luxury accessory production. Unlike bulk textile products, scarves—particularly those crafted from premium materials like silk and cashmere—require meticulous inspection of both functional and aesthetic attributes, including weave consistency, pattern alignment, and hand-feel.
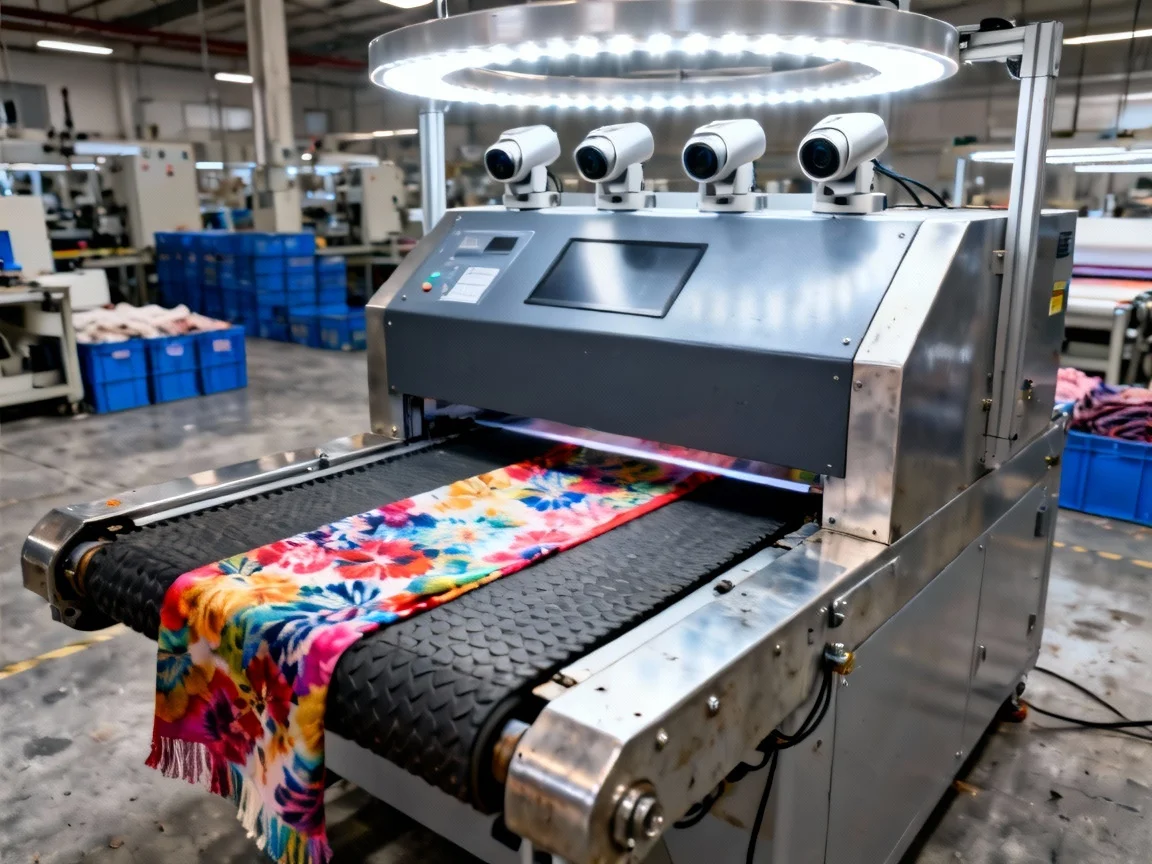

Quantifiable Performance Gains
Modern AI-powered inspection systems achieve defect detection accuracy rates of 80-95% for common textile imperfections, representing a significant improvement over manual inspection methods that typically reach just 60-75% accuracy. This performance difference translates directly to business outcomes: a leading industry analysis found textile manufacturers implementing automated quality control reduced overall production costs by up to 20%. These savings accrue through decreased material waste, fewer rework requirements, and optimized labor allocation—benefits that have an even more pronounced impact on profitability for scarf producers working with high-value materials.
Material-Specific Inspection Capabilities
Luxury scarf materials demand specialized inspection approaches. Silk, prized for its luster and drape, requires detection systems sensitive to subtle variations in thread tension and weave density that affect both appearance and durability. Wool and cashmere scarves demand precision in identifying fiber irregularities that compromise softness and warmth retention. Advanced multi-spectral imaging systems now offer material-specific analysis protocols, including adjustable lighting spectrums and magnification levels tailored to distinct quality parameters.
Sustainability and Compliance Benefits
Beyond operational efficiency, automated quality control supports the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices in fashion. By minimizing material waste through more precise defect identification, manufacturers significantly reduce their environmental footprint. The data logging capabilities of automated systems also provide comprehensive quality documentation, facilitating compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001—a benchmark for luxury brands and their suppliers. This documentation trail proves invaluable during customer audits and certification renewals, streamlining processes that traditionally relied on manual record-keeping.
Technical Assessment and System Design
Implementing an effective automated quality control system requires a methodical approach to technology selection and workflow integration, tailored to the specific requirements of scarf manufacturing. This phase establishes the foundation for successful deployment by aligning technical capabilities with production goals and material characteristics.
Comprehensive Needs Analysis
The initial assessment should begin with a thorough evaluation of current quality control processes to identify specific pain points and improvement opportunities. This analysis should quantify existing defect rates by category (e.g., weave irregularities, color variation, finishing defects) and track their impact on production costs and customer satisfaction. For scarf manufacturers, special attention must be paid to:
- Material variability: Establishing inspection parameters for each material type (silk, wool, cashmere, blends) and weave structure
- Design complexity: Adapting detection systems to distinguish between intentional design elements and actual defects
- Production volume: Determining throughput requirements to ensure inspection systems keep pace with manufacturing lines
- Quality thresholds: Defining acceptable defect levels based on customer expectations and market positioning
This data-driven assessment ensures automation investments target the highest-impact areas, maximizing return on investment while addressing critical quality issues.
Technology Selection Framework
Scarf manufacturers face a range of technology options for quality control automation, each with distinct capabilities and limitations. The optimal solution typically combines multiple technologies to address diverse quality requirements:
- High-resolution imaging systems: Capture detailed visual data at production line speeds, with minimum resolution requirements of 12 megapixels for pattern and print inspection
- AI-powered defect classification: Machine learning algorithms trained on scarf-specific defect libraries, capable of distinguishing between critical and non-critical imperfections
- Material testing integration: Systems for measuring fiber quality, thread count, and tensile strength, particularly important for luxury materials
- Color analysis tools: Spectrophotometric measurement to ensure consistency with color standards across production runs
- Data management platforms: Centralized systems for quality data storage, analysis, and reporting
When evaluating vendors, prioritize solutions with proven performance in textile applications, ideally with specific experience in accessory production. The selected system should offer configurable inspection parameters to accommodate different scarf styles, materials, and design complexities, along with intuitive operator interfaces that minimize training requirements.
Integration Planning
Successful automation implementation requires careful planning for integration with existing production workflows. Map the entire scarf manufacturing process to identify optimal inspection points, which typically include:
- Pre-production: Raw material inspection for fiber quality and consistency
- In-process: Real-time monitoring during weaving or printing to identify issues early
- Post-production: Comprehensive final inspection before packaging
For each inspection point, determine optimal system placement, lighting conditions, and throughput rates to minimize production disruption. In many cases, phased implementation provides the most practical path forward—begin with high-value or high-defect-rate processes to allow for iterative refinement before full-scale deployment.
Implementation Roadmap and Best Practices
The successful deployment of automated quality control systems in scarf manufacturing follows a structured implementation process that balances technical precision with operational practicality. Based on industry best practices and lessons learned from textile automation projects, this phased approach ensures minimal disruption to production while maximizing return on technology investment.
Phase 1: Infrastructure Preparation (4-6 weeks)
Before system installation, prepare both the physical production environment and data infrastructure to support automated inspection. This includes evaluating and potentially upgrading electrical systems to meet the power requirements of imaging equipment and computing hardware. Environmental controls may need enhancement to maintain consistent lighting conditions critical for visual inspection accuracy—particularly important in facilities with natural light exposure that creates variable conditions throughout the day.
Data infrastructure preparation involves establishing secure network connectivity between inspection stations and central servers, ensuring sufficient bandwidth to handle the large image files generated during inspection processes. For manufacturers implementing multiple inspection points, develop a unified database architecture that can aggregate quality data from across the production floor, enabling comprehensive analysis of defect trends and process performance.
Phase 2: System Deployment and Calibration (6-8 weeks)
Physical installation of inspection hardware should follow a detailed layout plan that minimizes disruption to existing workflows. For inline systems integrated with production machinery, coordinate with equipment manufacturers to ensure proper synchronization and safety interlocks. Pay particular attention to lighting configuration, as the reflective properties of silk and other luxury materials can create challenges for image analysis if not properly controlled.
The calibration process represents a critical step in ensuring system accuracy and reliability, involving:
- Establishing baseline image quality parameters for different scarf materials
- Creating material-specific inspection recipes that account for variations in texture, color, and weave
- Training defect classification algorithms using representative samples of both acceptable products and common defects
- Validating measurement accuracy against manual inspection standards and physical measurements
This calibration must address the unique characteristics of each product line, including size variations, pattern complexity, and material properties. The process should involve quality control personnel with intimate knowledge of product specifications to ensure the automated system aligns with customer expectations and brand standards.
Phase 3: Operator Training and Process Integration (4-6 weeks)
While automated systems reduce reliance on manual inspection, they introduce new technical requirements for operating and maintaining the technology. Develop a comprehensive training program for both quality control personnel and production staff, covering:

- System operation and monitoring
- Defect review and classification verification
- Basic maintenance and troubleshooting
- Data analysis and reporting interpretation
- System calibration for new product introductions
The training approach should combine classroom instruction with hands-on practice, allowing operators to gain confidence with the new technology while maintaining quality standards during the transition period. Establish a small team of "super-users" who receive advanced training and serve as internal experts for ongoing support.
Phase 4: Validation and Optimization (8-12 weeks)
Following system deployment, a validation period ensures the automated inspection process consistently meets quality requirements before full-scale implementation. Run parallel manual and automated inspections, compare results, and make necessary adjustments to sensitivity settings and defect classification criteria. During this period, establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure system effectiveness, such as:
- Defect detection accuracy rate
- False positive/negative percentages
- Inspection throughput
- Defect classification consistency
- Reduction in customer complaints or returns
Apply continuous improvement methodologies to optimize system performance over time. Regular review of quality data can identify recurring defect patterns that indicate upstream production issues, while feedback from operators helps refine the user interface and inspection processes. As new scarf designs and materials are introduced, regularly update and retrain the system to maintain inspection effectiveness.
Performance Metrics and ROI Analysis
The successful implementation of automated quality control systems must be evaluated through comprehensive performance monitoring and return on investment analysis, providing clear evidence of value creation while identifying opportunities for further optimization. For scarf manufacturers, this measurement framework should address both quantitative metrics and qualitative improvements that contribute to business success.
Key Performance Indicators
Establish a balanced set of KPIs to track the performance of automated quality control systems, focusing on metrics that directly impact business outcomes:
- Defect Detection Effectiveness:
- Overall accuracy rate compared to manual inspection
- Detection rates for specific defect categories relevant to scarves (e.g., pattern misalignment, thread tension variations)
- False positive/negative rates requiring review
- Operational Efficiency:
- Inspection throughput rates, measured in scarves per minute
- Reduction in inspection labor requirements
- Time savings in quality control processes
- Quality Improvement:
- First-pass yield improvements
- Reduction in customer complaints or returns
- Decrease in rework and scrap rates
- Compliance rates with quality standards
- Cost Metrics:
- Cost per inspection compared to manual methods
- Material savings from reduced waste
- Labor cost reductions
- Return on investment period
Track these metrics continuously using the data collection capabilities of the automated system, providing regular reporting to management to demonstrate ongoing value creation. For luxury scarf manufacturers, additional brand-specific metrics might include consistency with premium quality standards and reductions in quality-related production delays.
ROI Calculation Methodology
The return on investment for automated quality control systems in scarf manufacturing encompasses both direct financial benefits and indirect operational improvements. A comprehensive ROI analysis should consider:
- Initial Investment Costs:
- Hardware and software acquisition
- Installation and integration
- Training and change management
- Initial calibration and validation
- Ongoing Operational Costs:
- Maintenance and support contracts
- Consumables (lighting elements, cleaning supplies)
- Software updates and license fees
- Operator training for new product lines
- Quantifiable Benefits:
- Labor cost savings from reduced manual inspection
- Material savings from decreased scrap and rework
- Improved production throughput
- Reduced warranty claims and returns
- Energy efficiency gains from optimized processes
Industry benchmarks suggest textile manufacturers typically achieve ROI on quality control automation within 12-36 months, with scarf producers often seeing faster payback due to higher material costs and quality standards associated with luxury accessories. A case study from a mid-sized scarf manufacturer specializing in silk products reported achieving full ROI in 18 months through a combination of 35% reduction in inspection labor, 22% decrease in material waste, and 15% improvement in on-time delivery rates following automated system implementation.
Continuous Improvement Framework
Maximize the long-term value of automated quality control investments by establishing a structured continuous improvement program, leveraging the rich data generated by these systems through:
- Regular Performance Reviews: Scheduled analysis of quality metrics to identify improvement opportunities and address emerging issues before they impact customers.
- Root Cause Analysis: Systematic investigation of recurring defects to identify and correct upstream production issues, rather than simply detecting and sorting defective products.
- Technology Updates: Staying current with software updates and periodic hardware upgrades to maintain system performance as manufacturing processes evolve.
- Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry standards and competitors to identify gaps and best practices.
- Employee Engagement: Encouraging operator feedback on system performance and potential improvements, leveraging their intimate knowledge of both the technology and the products.
Treat automated quality control as a strategic investment rather than a one-time technology purchase, allowing scarf manufacturers to continuously extract greater value from their systems while maintaining a competitive edge in quality and operational efficiency.
Quality Standards and Compliance Integration
In the luxury scarf market, where brand reputation and customer loyalty depend on consistent quality, integrating automated inspection systems with established standards is essential. This alignment ensures technological investments translate into meaningful quality improvements recognized by both customers and regulatory bodies.
International Standards Alignment
Configure automated quality control systems to support compliance with relevant international standards governing textile production and quality management. The cornerstone of these standards is ISO 9001, which provides a framework for establishing, implementing, and maintaining effective quality management systems. For scarf manufacturers, ISO 9001 compliance requires documented quality processes, consistent measurement methods, and traceability throughout the production cycle—areas where automated inspection systems provide significant advantages.
Beyond general quality management, consider material-specific standards that impact inspection requirements:
- ISO 18640 for textile care labeling, ensuring quality claims regarding durability and maintenance are substantiated by inspection data
- OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 for product safety, requiring inspection protocols for harmful substances in materials
- ISO 105 series for textile color fastness testing, which can be integrated with automated color measurement systems
- ASTM D1776 for standard test methods for textile fabrics, providing guidelines for inspection procedures
The data logging capabilities of automated systems prove invaluable for compliance documentation, generating comprehensive quality records that demonstrate adherence to standards during audits and certification processes. Configure systems to capture specific measurements required by relevant standards to streamline compliance activities that traditionally relied on manual testing and documentation.
Customer-Specific Quality Agreements
Luxury scarf manufacturers often work with premium brands and retailers that impose additional quality requirements beyond industry standards. Automated inspection systems should be flexible enough to accommodate these customer-specific criteria, which may include:
- Acceptable Quality Levels (AQL): Customer-defined defect thresholds, typically more stringent for luxury goods (often 1.0 or 0.65 AQL for critical defects)
- Visual standards: Subjective quality attributes translated into quantifiable measurements
- Performance requirements: Specific durability or functional criteria
- Packaging specifications: Inspection of folding, labeling, and presentation elements
Advanced systems allow for the creation of customer-specific inspection recipes that can be quickly loaded when producing orders for different clients. This customization extends to reporting formats, generating quality documentation tailored to each customer's requirements and facilitating communication between manufacturers and brands.
Material-Specific Quality Parameters
The diverse range of materials used in luxury scarf production demands specialized inspection approaches addressing unique quality characteristics:
- Silk scarves require detection systems sensitive to:
- Thread tension variations that affect drape
- Subtle color variations in printed designs
- Selvage quality and edge finishing
- Pinholes and snags that compromise appearance
- Wool and cashmere scarves demand attention to:
- Fiber alignment and density
- Pilling potential and surface smoothness
- Thickness consistency across the product
- Luster variations indicating fiber quality
- Blended fabrics require inspection protocols that:
- Verify material composition percentages
- Ensure consistent distribution of component fibers
- Address quality characteristics of each material type
Modern inspection systems offer material-specific algorithms and lighting configurations that optimize detection capabilities for different requirements. By creating and storing material-specific inspection parameters, manufacturers ensure consistent quality assessment across their product range while accommodating the unique characteristics of each material.
Future Trends and Continuous Improvement
The landscape of quality control automation continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technologies. For scarf manufacturers committed to maintaining competitive advantage through quality excellence, staying abreast of these developments and incorporating them into long-term quality strategies is essential.
Emerging Technologies Shaping Quality Control
Several technological trends are poised to transform automated quality control in the textile industry, with particular relevance to scarf manufacturing:
- Advanced Computer Vision: Next-generation imaging systems incorporating hyperspectral and multispectral cameras that capture data beyond the visible spectrum, enabling detection of subsurface defects and material inconsistencies not visible to traditional systems. For luxury scarves, this technology offers the potential to identify quality issues in premium materials before they become visible to consumers.
- Deep Learning Evolution: Continued advancement in neural network architectures specifically optimized for textile inspection, showing improved ability to distinguish between intentional design elements and actual defects—a critical capability for patterned scarf designs. These systems will increasingly learn from manufacturer-specific defect patterns, improving accuracy over time.
- Edge Computing: Moving processing capabilities closer to inspection points reduces latency and enables real-time adjustment of upstream production processes based on quality data. For scarf manufacturers, this means potential quality issues can be addressed immediately, minimizing waste and improving overall process control.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of production processes that integrate quality data to simulate and optimize inspection strategies. This technology allows manufacturers to test new inspection approaches virtually before implementing them on the production floor, reducing implementation risk for new scarf designs or materials.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: Combining automated inspection with AR interfaces that guide operators to identified defects, improving efficiency of manual review processes and facilitating operator training.
These technologies promise to further enhance inspection accuracy, reduce false positives, and provide deeper insights into quality issues, ultimately driving continuous improvement in scarf manufacturing processes.
Building a Culture of Quality Excellence
Technology alone cannot ensure sustained quality improvement without a corresponding focus on organizational culture and people development. Manufacturers should complement automated systems with initiatives that foster quality意识 throughout the organization, including regular training programs, cross-functional quality teams, and incentive structures that reward quality achievements. By integrating technology with a strong quality culture, scarf manufacturers can create a sustainable competitive advantage that drives business success in the luxury textile market.