In the dynamic landscape of fashion accessories manufacturing, the choice between digital and traditional printing technologies for scarf production has evolved into a strategic decision with far-reaching implications. As consumer expectations for customization, rapid delivery, and environmental responsibility continue to escalate, understanding the technical capabilities and economic trade-offs of each printing method is essential for maintaining competitive advantage. This analysis synthesizes current industry data and manufacturing insights to provide fashion businesses with actionable intelligence for optimizing their production strategies.
Technical Foundations: Understanding the Printing Processes
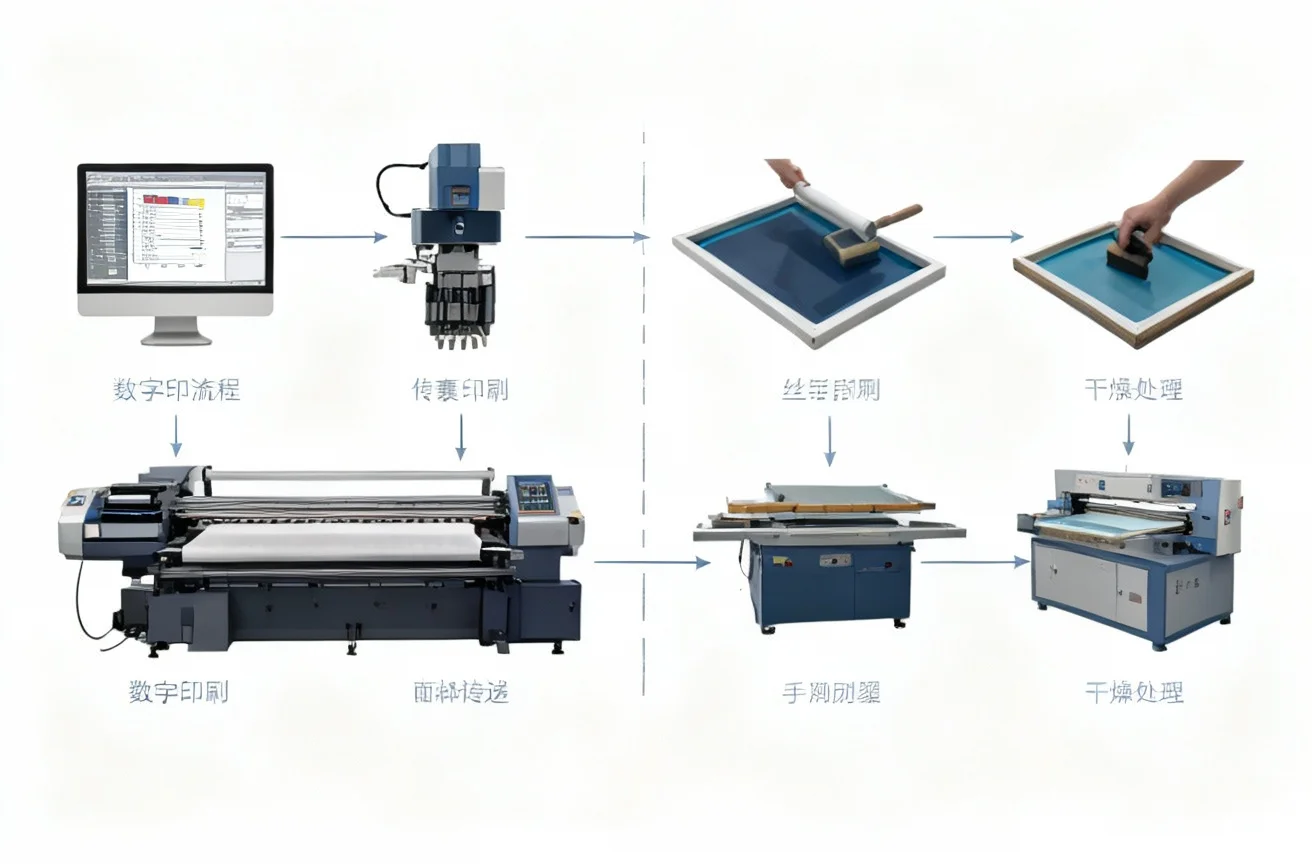
Digital textile printing represents a paradigm shift in textile decoration, fundamentally transforming how designs are transferred to fabric substrates. Unlike conventional screen printing, which relies on physical stencils for each color separation, digital systems utilize advanced inkjet technology to deposit pigmented inks directly onto textiles. This digital workflow eliminates numerous production steps, significantly reducing both setup time and material waste while enabling unprecedented design freedom.
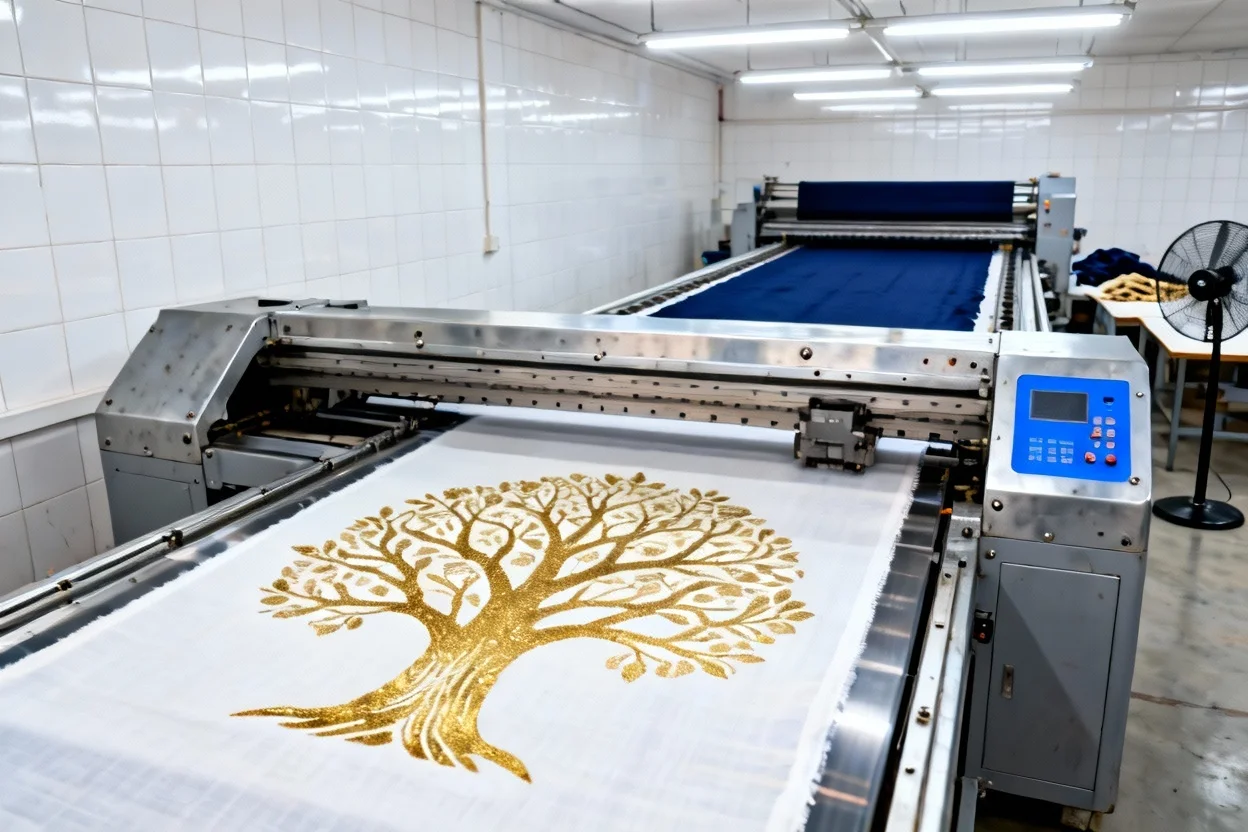

Traditional printing methods, predominantly screen printing, have served as the industry backbone for decades, valued particularly for their efficiency in high-volume production scenarios. The process involves creating a separate mesh screen for each color component of a design, applying ink through these screens onto the fabric, and repeating for each color layer. While highly effective for large production runs with limited color variations, this method becomes increasingly cumbersome and cost-prohibitive with complex designs or frequent design changes.
These technical distinctions translate directly into operational capabilities. Digital systems excel at reproducing intricate patterns with unlimited color gradients that would be either impossible or excessively expensive to achieve with traditional methods. Modern digital printers achieve resolutions up to 1200 dpi, capturing fine details that remain crisp even on delicate luxury fabrics such as silk and cashmere—materials frequently specified in high-end scarf production.
Economic Analysis: Cost Structures and Production Economics
The economic equation between digital and traditional printing encompasses more than simple per-unit costs, involving complex calculations of setup expenses, production volumes, and design complexity. Traditional screen printing requires substantial upfront investment in screen production, setup, and color mixing, creating a cost structure that favors large production runs. Industry benchmarks indicate that screen printing typically becomes cost-effective at quantities exceeding 500 units per design, with average setup costs ranging from $300-800 per design depending on color complexity.
Digital printing eliminates these initial setup expenses, positioning it as the more economical choice for small to medium production volumes. According to 2025 manufacturing data, digital printing reaches cost parity with traditional methods at approximately 300 units for standard designs. Notably, digital per-unit costs remain relatively stable across production volumes, creating a flat cost curve that supports on-demand production models and limited-edition collections.
A comparative analysis of production costs for a mid-sized fashion brand illustrates this dynamic. For a run of 100 scarves featuring a 12-color design, digital printing delivered a 47% lower total production cost compared to screen printing. Conversely, for a classic 3-color design produced in quantities of 1000 units, traditional methods maintained a 23% cost advantage. These findings underscore the importance of aligning printing technology with both production volume requirements and design complexity.
Quality Parameters: Aesthetic and Functional Considerations
The tactile and visual characteristics of printed scarves significantly influence market positioning and perceived product value. Traditional screen printing typically produces thicker ink deposits, creating a more pronounced texture on the fabric surface. This quality can enhance certain design aesthetics and provides excellent color saturation, particularly on natural fibers like cotton and wool.
Digital printing technology has made substantial quality advancements, now offering superior color accuracy and detail reproduction capabilities. The precision ink placement achieves gradients and subtle color transitions that remain challenging with traditional methods. High-resolution digital printing preserves the natural drape and hand feel of luxury fabrics—a critical factor for high-end scarf production where fabric quality is paramount to brand identity.
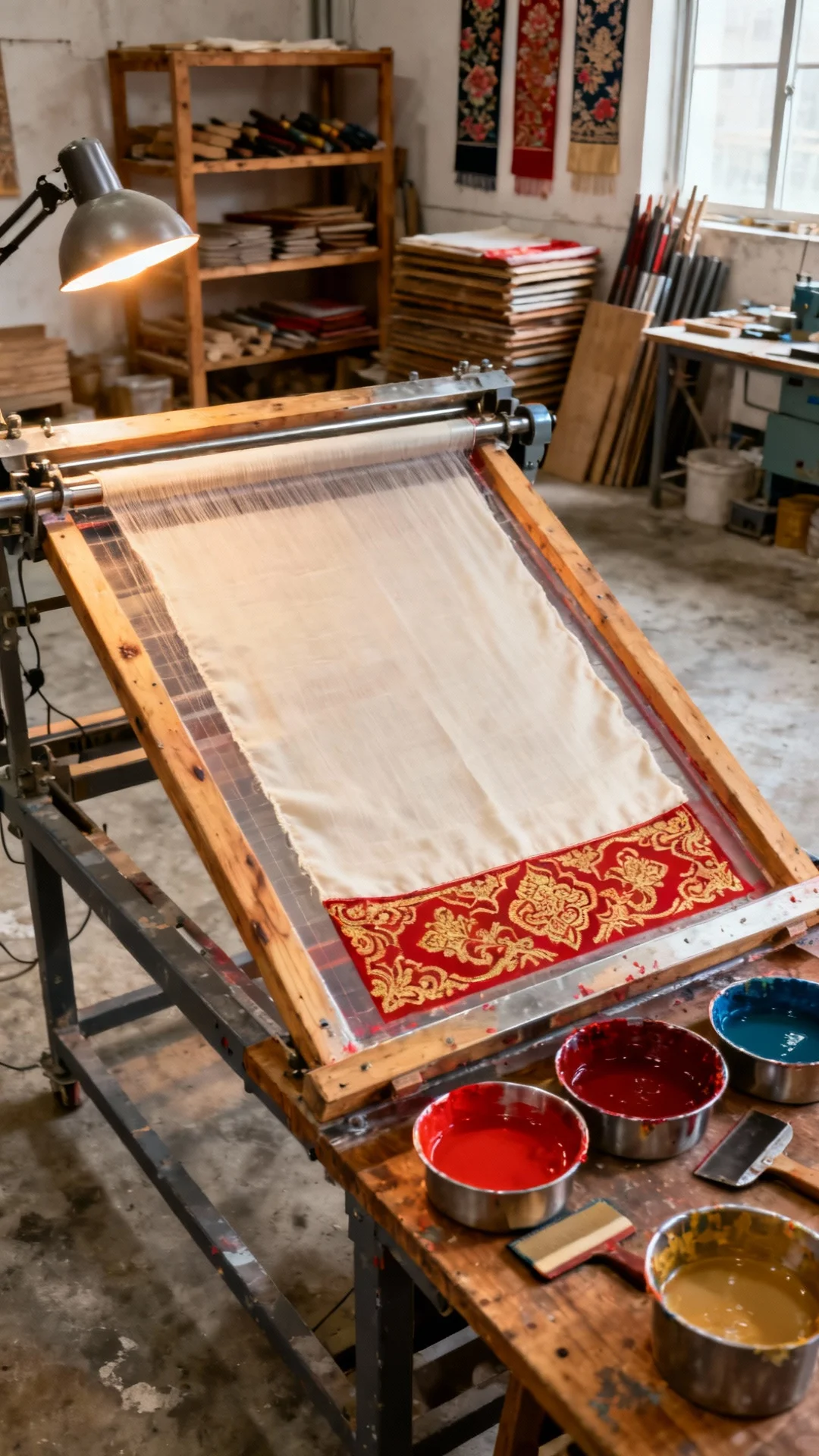

Independent textile laboratory testing reveals nuanced performance differences between the methods. Traditional printing generally exhibits slightly better wash fastness ratings (ISO 105-C06), particularly with reactive dyes on cotton substrates. Digital printing using pigmented inks, however, offers superior light fastness (ISO 105-B02), maintaining color vibrancy longer under prolonged sunlight exposure—a significant advantage for accessories frequently worn outdoors.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Metrics and Eco-Footprint
The environmental footprint of textile production has emerged as a decisive factor for environmentally conscious brands and consumers. Digital printing demonstrates substantial sustainability advantages across multiple metrics, most notably in water consumption. Industry studies confirm that digital textile printing reduces water usage by 85-90% compared to traditional screen printing methods, which require extensive water for screen preparation, color mixing, and post-printing washing processes.
Energy consumption presents a more balanced picture. Digital systems require significant electricity for operation but eliminate the energy-intensive drying steps necessary for traditional printing. Carbon footprint analyses indicate digital printing achieves a 30-40% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions for typical production runs, with the gap widening for smaller batches due to reduced material waste.
Waste reduction represents another environmental benefit of digital technology. Traditional screen printing generates substantial pre-production waste from screen preparation and color testing, while digital systems minimize material usage through precise ink deposition and digital proofing. Post-consumer sustainability also favors digital production, as its on-demand capabilities reduce overproduction and inventory waste—major contributors to fashion industry landfill accumulation.
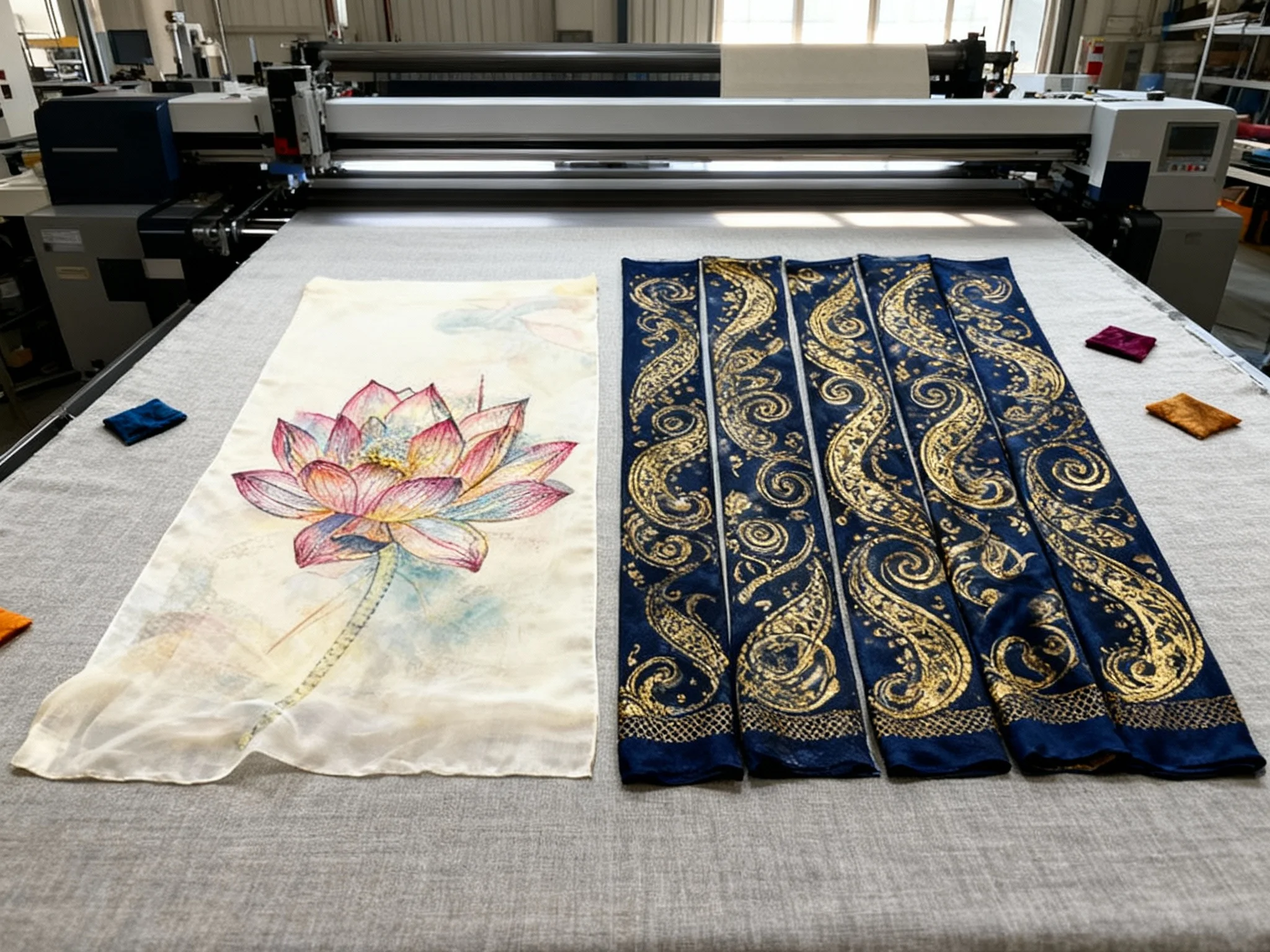

Production Workflow and Operational Agility
Integrating digital printing technology fundamentally transforms production workflows, enabling unprecedented operational agility. Traditional printing requires extensive pre-production preparation, including screen creation, color separation, and setup, resulting in typical lead times of 2-4 weeks for custom designs. This extended timeline limits brands' ability to respond quickly to emerging trends or shifting consumer demands.
Digital printing systems dramatically compress production cycles, with lead times of 3-5 days becoming standard for small to medium runs. This rapid turnaround enables innovative business models like on-demand scarf production, where items are manufactured only after customer orders are received, eliminating inventory risks. The digital workflow also facilitates easy design modifications and versioning, supporting limited-edition releases and personalized customization options.
Automation integration further enhances digital production efficiency. Modern digital printing facilities utilize Industry 4.0 technologies, including automated material handling, AI-driven color calibration, and integrated quality control systems. These advancements reduce labor requirements while improving consistency and production throughput—a combination redefining manufacturing economics for scarf production.
Strategic Technology Adoption: Aligning with Business Objectives
The decision to adopt digital or traditional printing technology should be guided by a comprehensive assessment of production requirements, market positioning, and long-term business objectives. Brands specializing in fast-fashion accessories with frequent design rotations and small batch sizes will find digital printing's flexibility and rapid turnaround capabilities indispensable for meeting market demands.
For luxury brands producing iconic designs with stable demand, traditional printing may still offer advantages in cost efficiency for large runs and specific tactile qualities. However, growing consumer emphasis on sustainability and customization is pushing even established luxury houses to incorporate digital technology into their production portfolios.
Hybrid production models represent an emerging trend, leveraging the strengths of both technologies. This approach uses digital printing for prototyping, limited editions, and custom orders while maintaining traditional capabilities for high-volume core designs. Implementing such a flexible manufacturing strategy requires careful planning but gives brands the agility to address diverse market needs efficiently.
Future Trends: Technological Evolution in Scarf Printing
The digital textile printing sector continues to evolve rapidly, with ongoing innovations addressing current limitations. Advancements in ink technology are expanding the range of printable fabrics, with new formulations offering improved performance on challenging substrates like silk and polyester. Print speed enhancements are narrowing the production gap between digital and traditional methods, making digital increasingly viable for medium-volume production.
Integration of smart technologies is further transforming digital printing capabilities. AI-powered design optimization tools can automatically adjust patterns for optimal printing efficiency, while IoT-enabled production systems provide real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. These intelligent manufacturing solutions drive productivity gains and reduce operational costs while improving quality control.
Sustainability innovations in digital printing include developing bio-based inks, energy-efficient curing systems, and closed-loop water recycling. These advancements progressively address the remaining environmental impacts of digital production, moving the industry closer to true circular manufacturing models.
Implementation Guidelines for Fashion Businesses
When transitioning to digital printing technology, brands should conduct a thorough assessment of their specific requirements, including design complexity, production volumes, and quality standards. Engaging with experienced technology partners and conducting small-batch trials can help identify potential challenges and optimization opportunities before full-scale implementation.
Investment in color management systems is critical for ensuring consistent results across production runs and maintaining brand color standards. Implementing robust digital asset management practices will maximize the benefits of digital workflow, enabling efficient design versioning and rapid production setup.
Staff training should not be overlooked, as digital printing requires different technical skills than traditional methods. Developing expertise in digital design preparation, ink management, and maintenance procedures will ensure optimal performance and return on investment.
The choice between digital and traditional printing for scarf production represents a strategic decision influencing manufacturing operations, product development, market responsiveness, and environmental impact. While traditional methods continue to hold value for specific applications, digital printing technology offers compelling advantages in flexibility, sustainability, and operational efficiency that align with the evolving needs of the fashion industry. By carefully evaluating production requirements against each technology's capabilities, brands can implement an optimal printing strategy balancing quality, cost efficiency, and sustainability—positioning themselves for success in an increasingly competitive marketplace.