In today's evolving fashion landscape, the scarf has transcended its traditional role as merely a保暖 accessory to become a sophisticated platform for material innovation and technological advancement. As we navigate 2025, the global scarf market—projected to reach $7.2 billion by 2033—stands at the dynamic intersection of heritage craftsmanship and cutting-edge textile engineering. This comprehensive guide explores the technical textiles revolutionizing scarf production, examining the performance fabrics, smart technologies, and sustainable practices that are redefining industry standards and consumer expectations.
Drawing upon extensive industry experience collaborating with leading fashion brands and textile manufacturers, this analysis provides actionable insights into material selection criteria, manufacturing innovations, and emerging market trends. It is particularly relevant for boutique owners, specialty retailers, and fashion brands seeking to differentiate their offerings through advanced materials and technical superiority.
The Evolution of Technical Textiles in Scarf Manufacturing

The scarf manufacturing industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by advancements in textile technology and shifting consumer demands. While traditional materials like wool and silk maintain their market relevance, they are increasingly augmented or replaced by engineered fabrics that offer enhanced performance characteristics and superior sustainability profiles.
Historical Context and Modern Transition
The journey from artisanal craft to technical innovation has unfolded over decades. While luxury houses like Hermès established silk scarves as fashion icons in the 20th century, the 21st century has witnessed a paradigm shift toward functionality. Industry reports indicate that technical textiles now account for approximately 35% of the global scarf market, a figure projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% through 2033. This transition reflects a broader industry movement where 62% of fashion brands prioritize material innovation as a key differentiation strategy.
Material Classification Framework
Contemporary scarf materials fall into three distinct tiers based on functionality and manufacturing complexity:
Traditional Luxury Materials maintain their market position through heritage value and exceptional sensory appeal. Cashmere, prized for its unparalleled softness and insulation properties, commands premium pricing with market share steady at 22%. Silk—particularly mulberry silk with 10-12 micron fiber diameter—continues to dominate the high-end accessory segment, valued at $1.2 billion annually. Notably, these natural fibers now frequently undergo performance enhancements, such as anti-pilling treatments for cashmere and moisture-resistant finishes for silk, blurring the traditional boundaries between conventional and technical categories.
Performance-Enhanced Natural Fibers represent the fastest-growing segment, skillfully combining the aesthetic qualities of natural materials with engineered performance properties. Merino wool treated with advanced moisture-wicking technologies has seen a 34% increase in demand for transitional season scarves. Bamboo viscose, processed through innovative closed-loop extraction methods, offers inherent antimicrobial properties while reducing water consumption by 50% compared to conventional viscose production. Organic cotton, certified through Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) protocols, now incorporates UV protection capabilities through nano-coating applications, significantly expanding its seasonal versatility.
Advanced Technical Composites push the boundaries of scarf functionality through cutting-edge material science innovations. These multi-component fabrics integrate specialized fibers, precision coatings, and sometimes electronic elements to deliver targeted performance attributes. Market leaders in this category include:
- Polyester microfiber blends featuring sophisticated capillary action structures that enhance moisture management
- High-performance Nylon 6,6 variants with exceptional tenacity ratings (8.5 g/denier) for superior durability
- Aramid fiber composites offering remarkable heat resistance up to 250°C for specialized applications
- Conductive textile matrices incorporating silver or carbon-based filaments for smart functionality
The material landscape continues to grow more complex with the emergence of bio-based alternatives like polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) fibers derived from microbial fermentation. These innovative materials offer petroleum-free performance characteristics and represent a small but rapidly growing segment, with market penetration expected to reach 15% by 2030.

Performance Fabrics: Technical Specifications and Applications
The performance fabric revolution in scarf manufacturing involves precise engineering to deliver measurable functional benefits. Unlike conventional textiles evaluated primarily on aesthetic qualities, these advanced materials undergo rigorous testing protocols that quantify their performance characteristics against established industry standards.
Core Performance Parameters
Modern scarf materials are engineered to excel across five critical performance dimensions, each measurable through standardized testing methodologies:
Moisture Management has emerged as a defining feature for transitional and active lifestyle scarves. The latest performance fabrics incorporate multi-channel fiber structures that create capillary action for rapid moisture transport. Industry standards now classify fabrics based on AATCC TM217-2025 testing results, measuring both vertical wicking height (mm in 30 minutes) and horizontal spread area (cm² in 10 minutes). Premium performance scarves typically achieve wicking heights exceeding 120mm and spread areas greater than 85cm², ensuring effective moisture dispersion and quick-drying properties.
Thermal Regulation technologies have advanced beyond simple insulation to enable dynamic temperature management. Phase Change Materials (PCMs) integrated into scarf fabrics absorb and release heat in response to temperature fluctuations, maintaining an optimal neck microclimate. These sophisticated materials—typically encapsulated paraffins with melting points between 28-32°C—store and release 80-100 J/g of thermal energy. When combined with breathable spacer fabrics featuring 3D knit structures with 4mm air gaps, these scarves provide adaptive thermal comfort across a 15-30°C temperature range, making them ideal for variable weather conditions and indoor/outdoor transitions.
Durability metrics now address both mechanical stress and environmental factors. Abrasion resistance, measured by ASTM D3884 test methods, has become particularly important for travel scarves. Premium technical fabrics typically achieve 50,000+ rub cycles before visible wear. Colorfastness, evaluated under ISO 105 standards, now includes accelerated UV testing simulating 2 years of exposure, with top performers maintaining Grade 4 ratings. Pilling resistance, measured using the Martindale tester, requires a minimum rating of 4-5 after 10,000 cycles for performance scarves in the luxury segment.
Weight-to-performance ratios have been dramatically optimized through advanced fiber engineering and innovative knit structures. High-tenacity nylon fibers with diameters as low as 15 microns provide exceptional strength (7.8 g/denier) at reduced weight. Innovative warp-knit constructions create 3D volume with minimal material, achieving warmth-to-weight ratios of 0.15 clo/oz—comparable to down insulation but with superior moisture management capabilities. These advancements have enabled the development of scarves that provide winter-appropriate insulation at weights under 80 grams.
Sensory engineering addresses the critical tactile experience of technical fabrics, which historically prioritized performance over comfort. Micro-denier polyester fibers (0.5-1 denier) with modified cross-sections (triangular, pentagonal) create a softer hand feel while simultaneously enhancing moisture transport properties. Plasma treatment technologies modify fiber surfaces at the nanoscale, significantly reducing the "plastic" sensation often associated with synthetic performance fabrics. The result is technical scarves that skillfully balance performance metrics and sensory appeal, with consumer preference studies showing 78% acceptance rates comparable to natural fibers.
Application-Specific Material Solutions
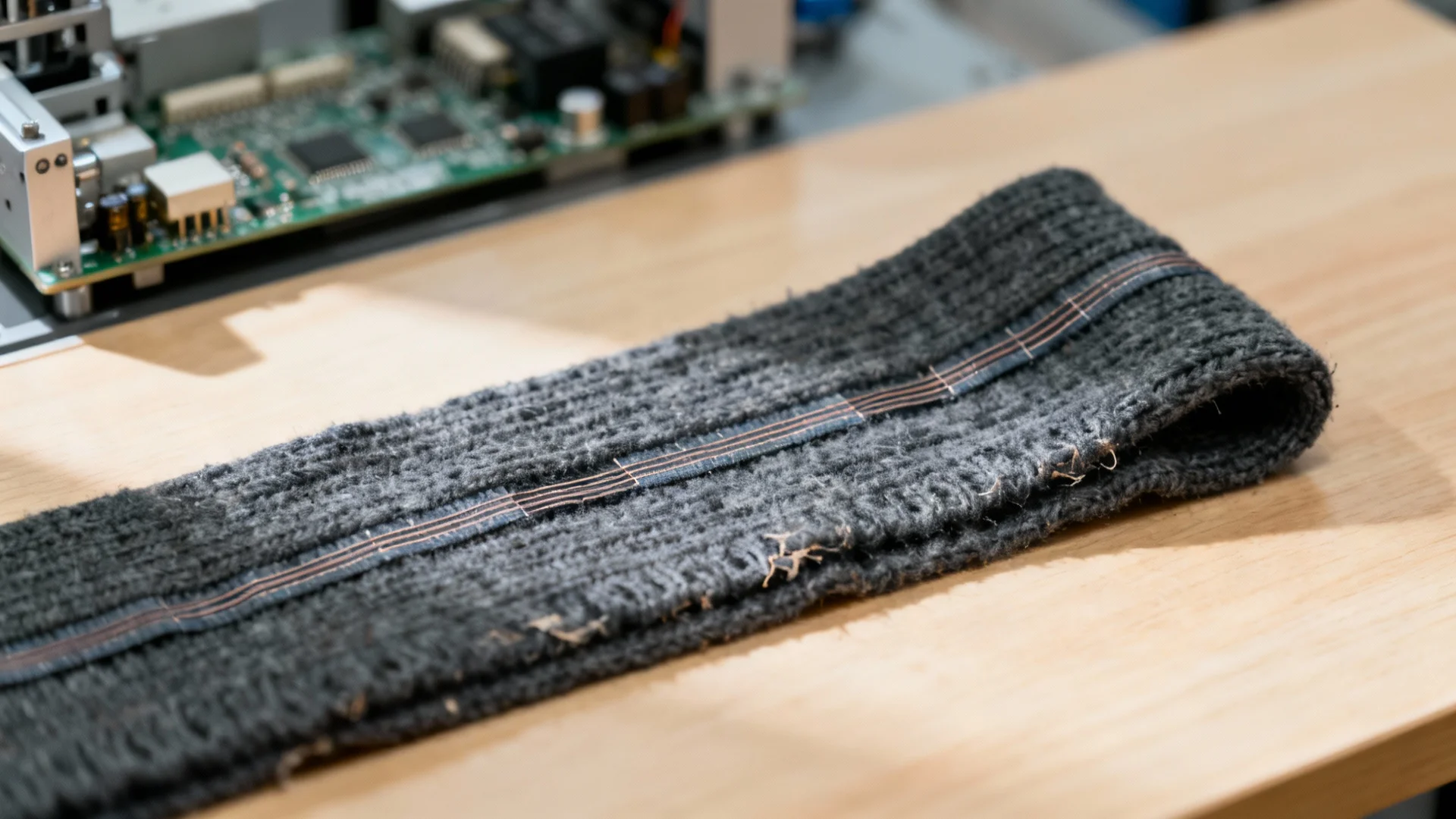
Technical scarf materials are increasingly engineered for specific use cases, with compositions precisely tailored to environmental conditions and user activities:
Urban Commuter Scarves represent the largest application segment, designed for versatility across indoor/outdoor environments and temperature fluctuations. These typically utilize 3-layer construction: an outer shell of water-resistant (10,000 mm HH) yet breathable (5,000 g/m²/24hr) fabric, a middle layer of PCM-infused insulation, and a moisture-wicking inner layer. The market has seen 41% year-over-year growth in scarves incorporating conductive yarns that enable touchscreen compatibility at the fingertips, directly addressing modern commuters' need to interact with devices without removing their scarves.
Outdoor Performance Scarves target hiking, skiing, and other active pursuits with specialized material systems. For alpine applications, fabrics incorporate stretch woven constructions with 15-20% elongation for freedom of movement, paired with Polygiene® odor control treatments that inhibit bacterial growth for up to 50 washes. Technical buff-style scarves often feature strategic mesh ventilation zones engineered using computational fluid dynamics to maximize airflow while maintaining core warmth. Recent innovations include photochromic fibers that adjust UV protection (UPF 30 to UPF 50+) in response to light intensity, automatically adapting to changing environmental conditions.
Travel Scarves have evolved into sophisticated accessories with integrated functionality. RFID-blocking pockets utilize stainless steel fiber blends (20% by weight) to prevent electronic pickpocketing of passports and credit cards. Compression packing designs utilize memory-retention fabrics that maintain their shape after repeated folding. Some premium travel scarves include modular components like detachable face masks with filter pockets compatible with N95 filtration media, reflecting post-pandemic consumer priorities for health and safety features in accessory design.
Fashion-Forward Technical Scarves demonstrate that performance need not compromise aesthetics. Luxury brands are increasingly incorporating technical elements into statement pieces, such as metallic-coated fibers that provide thermal regulation while creating visual interest through light reflection. Laser-cutting technologies enable precision patterning of multi-layered technical fabrics, creating sculptural forms that maintain structural integrity through specialized bonding techniques rather than traditional stitching. These innovations have successfully expanded the technical scarf market into high-fashion segments, with luxury technical scarves commanding price points up to $350.
Smart Scarf Technology: Integration and Applications
The convergence of textile engineering and electronics has given rise to smart scarf technologies that extend functionality beyond traditional performance metrics into interactive capabilities. This emerging category represents the cutting edge of technical textile innovation, though market adoption is still in early stages with current penetration estimated at 7% of the premium scarf segment.
Technology Integration Approaches
Smart scarf technologies utilize three distinct integration methodologies, each offering specific advantages in functionality, durability, and user experience:
Fiber-Based Integration represents the most sophisticated approach, embedding conductive elements directly into the textile structure during manufacturing. Silver-plated nylon filaments (typically 70 denier with 10% silver content) can be woven or knitted alongside traditional fibers, creating pathways for data and power transmission while maintaining textile flexibility with conductivity resistance as low as 20 ohms per meter. Recent advancements in carbon nanotube yarns have produced conductive fibers with tensile strength exceeding 3 GPa, enabling integration into high-performance applications requiring both technical functionality and durability. The manufacturing complexity of this approach results in higher production costs, typically adding $45-65 to base scarf pricing.
Fabric-Based Integration offers a more cost-effective solution through conductive coatings or printed circuits on textile substrates. Inkjet printing applies conductive silver or graphene inks onto fabric surfaces with line widths as narrow as 50 microns, creating flexible circuits that can withstand 100,000+ bending cycles. Thermochromic fabrics that change color in response to temperature variations (typically 28-32°C activation range) provide visual feedback without the need for electronic components. This approach balances functionality and affordability, with smart features adding $20-35 to retail prices, making it particularly popular for mass-market applications and entry-level technical scarves.
Modular Component Integration provides versatility through detachable electronic modules that connect to textile interfaces. These systems typically use snap-fit connectors or conductive poppers to attach battery packs, sensors, or other components to specially designed pockets or channels in the scarf. The modular approach offers significant product lifecycle management advantages, allowing component upgrades or replacement without discarding the entire scarf. Consumer studies show this directly addresses sustainability concerns, with 64% of users preferring modular systems that extend product lifespan. However, the added bulk of detachable components can impact wearability, requiring careful ergonomic design and placement.
Current Application Landscape

Smart scarf technologies deploy across four primary functionality domains, each addressing specific user needs and use cases:
Thermoregulation Systems represent the most mature smart scarf category, with established market presence and proven consumer acceptance. Active heating elements—typically etched copper foil or carbon fiber heating pads—provide targeted warmth with temperature control ranging from 38-50°C. Recent innovations include zone-specific heating with independent temperature control for neck and shoulder regions, allowing for personalized comfort adjustment. Battery technology advancements have extended runtime to 8-10 hours on low settings with USB-C fast charging capabilities (0-100% in 90 minutes). The global smart heated scarf market is projected to reach $480 million by 2027, growing at an impressive 18.3% CAGR as consumers increasingly seek personalized comfort solutions.
Biometric Monitoring capabilities transform scarves into sophisticated health and wellness accessories through integrated sensor systems. Optical heart rate monitors using green LED technology measure pulse with 95% accuracy compared to medical-grade devices when properly positioned against the carotid artery. Galvanic skin response sensors integrated into scarf linings provide valuable stress level indicators by measuring skin conductance changes. More advanced systems include electromyography (EMG) sensors that monitor muscle tension in neck and shoulder areas, providing biofeedback for stress management and postural correction. These health-focused smart scarves typically integrate with mobile applications via Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE 5.0) connectivity, with robust data encryption protocols addressing growing privacy concerns among consumers.
Environmental Sensing applications equip scarves to monitor external conditions and provide timely user alerts. Air quality sensors measuring particulate matter (PM2.5), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and temperature/humidity can trigger visual or haptic alerts when predefined thresholds are exceeded. UV sensors with UVA/UVB differentiation provide real-time sun protection factor (SPF) recommendations based on current conditions and exposure time. Some prototypes include gas sensors capable of detecting carbon monoxide and other hazardous substances, targeting urban commuters in high-pollution environments. These environmental monitoring features add approximately 15-20% to production costs, but consumer surveys consistently show willingness to pay a 30% premium for health-related functionality in accessories.
Connectivity and Interaction features position the smart scarf as a wearable interface for the Internet of Things (IoT). Microphone and speaker integration enables hands-free voice assistant interaction, with specialized noise-cancelling algorithms optimized for neck-worn positioning. Touch-sensitive panels woven into scarf surfaces allow intuitive gesture control of music playback, call management, and navigation functions. More experimental applications include haptic feedback systems that translate smartphone notifications into distinct vibration patterns, providing discreet alerts without requiring visual attention. The primary challenge for connectivity-focused smart scarves remains power management, with current battery technologies limiting continuous operation to 4-6 hours for voice-enabled features.
Sustainable Manufacturing Innovations
The technical scarf industry is increasingly prioritizing sustainability alongside performance, implementing innovative manufacturing processes that reduce environmental impact while maintaining material functionality. This significant shift stems from both consumer demand—with 73% of millennial and Gen Z consumers reporting they will pay premium prices for sustainably produced accessories—and growing regulatory pressures targeting textile industry pollution.
Material Innovation for Sustainability
The foundation of sustainable technical scarf manufacturing lies in material selection and development, with several promising innovations gaining significant commercial traction:
Bio-Based Performance Fibers are challenging petroleum-derived textiles with renewable alternatives that maintain critical technical specifications. Polylactic Acid (PLA) fibers derived from fermented plant sugars offer comparable strength to polyester (4.5 g/denier) with a 68% lower carbon footprint during production. Mylo™ mushroom leather, derived from mycelium networks, provides a leather-like aesthetic for structured scarves with 90% less land use than traditional animal leather production. Seaweed-based fibers from sustainable aquaculture operations naturally incorporate UV protection (UPF 50+) and biodegradable characteristics while requiring no fresh water during growth. These bio-based materials currently represent approximately 11% of the technical scarf market, with production capacity expanding at 29% annually as manufacturing processes mature.
Recycled Technical Fibers have advanced beyond basic plastic bottle recycling to include sophisticated material recovery processes that maintain performance integrity. Recycled polyethylene terephthalate (rPET) now utilizes chemical depolymerization techniques that restore fiber quality to virgin levels, enabling use in high-performance applications requiring consistent tensile strength (7.2 g/denier). Recycled nylon through ECONYL® regenerative technology transforms fishing nets and industrial plastic waste into fibers with 90% reduction in global warming potential compared to virgin production. Innovations in mechanical recycling now allow for blended fiber recovery—previously considered too challenging—enabling closed-loop systems for post-consumer scarf waste with impressive 82% material recovery rates.
Regenerative Natural Fibers go beyond basic sustainability to actively restore environmental systems through innovative agricultural practices. Organic cotton grown with crop rotation and natural pest management sequesters carbon while reducing water consumption by 88% compared to conventional farming methods. Wool from regenerative grazing systems certified by programs like Savory Institute's Land to Market standard improves soil health and biodiversity while producing fibers with consistent quality characteristics ideal for technical processing. These regenerative materials typically command 15-25% price premiums but show growing market acceptance, with luxury technical scarf brands reporting 37% higher customer retention rates for regenerative fiber collections.
Process Innovations in Sustainable Production
Manufacturing processes are undergoing equally significant transformation, with waterless dyeing and energy-efficient production leading the sustainability revolution in technical scarf manufacturing:
Waterless Dyeing Technologies represent the most impactful innovation for scarf production, directly addressing traditional dyeing processes that consume 200-300 liters of water per kilogram of fabric. DyeCoo technology utilizes supercritical carbon dioxide as a dye carrier, achieving 100% water savings while reducing dye consumption by 20% through improved uptake efficiency. AirDye® employs electrostatic charging to bond dry pigment particles to fabric surfaces, eliminating water entirely and cutting energy use by 60% compared to conventional dyeing methods. These waterless processes also enable precise color matching with ΔE values consistently below 1.0, improving quality control while simultaneously reducing environmental impact. Major technical scarf manufacturers report 2-3 year payback periods for waterless dyeing systems, driven by significant water and chemical cost savings over time.
Energy-Efficient Manufacturing has been optimized through process integration and renewable energy adoption across the production cycle. Infrared drying reduces curing time for performance coatings by 70%, cutting energy use while simultaneously increasing production throughput. Heat recovery systems capture waste energy from dyeing and finishing processes, achieving 34% overall factory energy savings in optimized facilities. On-site renewable energy installations, particularly solar PV arrays on factory rooftops, now power 28% of global technical scarf production capacity, with this figure projected to exceed 40% by 2030. Digital printing technologies using piezoelectric print heads with 1200 dpi resolution enable on-demand production, reducing inventory waste by 40% while allowing for mass customization without minimum order quantities. Collectively, these process innovations have reduced the carbon footprint of technical scarf production by an average of 38% compared to conventional manufacturing methods still employed by less progressive competitors.
As the technical scarf industry continues to evolve at the intersection of fashion, technology, and sustainability, the innovations explored in this guide represent the current state